HOME > PRODUCTS > > MEMBRANE ELEMENT
MEMBRANE ELEMENT
PRESENTATION
Membranes are designed to separate, concentrate or fractionate a wide variety of liquids.
They serve as a fine barrier between miscible fluids that allow the preferential transport of one or more components, when applied as a pressure differential.
To complement or replace conventional chemical treatments, it is possible to perform filtration with microfiltration, ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes.
APPLICATIONS
Disinfection of dechlorinated water after activated carbon filter;
Destruction of chlorine or ozone in water;
Water treatment plants;
Reduction of organic load in the water;
Manufacture of water-based paints and pigments;
Protection of reverse osmosis systems;
Disinfection of DI water in e-coat / KTL paint;
Removal of salts;
TYPES OF MEMBRANE FILTRATION
-
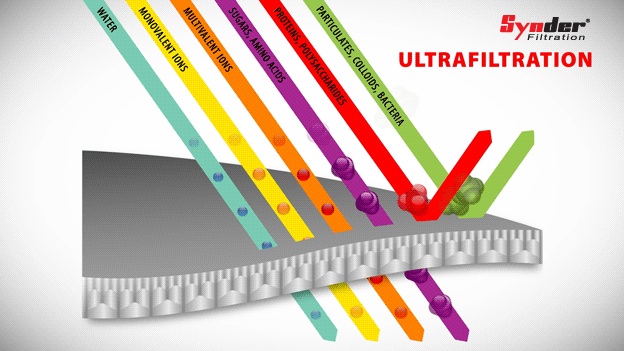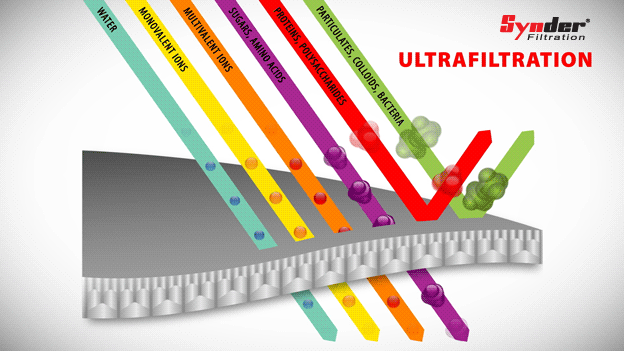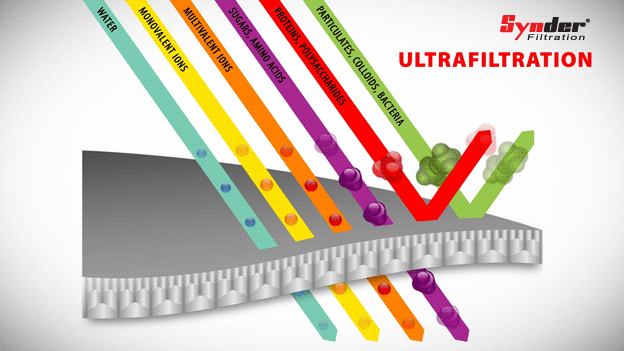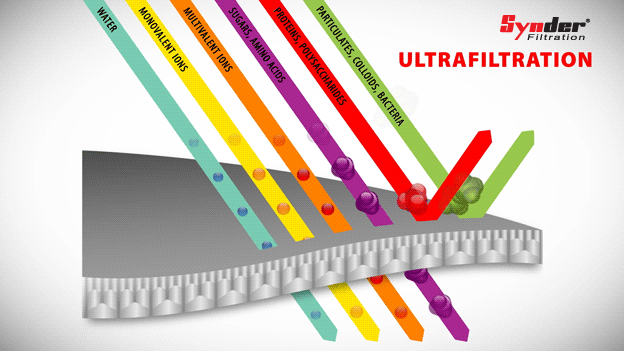
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration membranes are capable of separating larger materials, such as colloids, particles, fats, bacteria and proteins, while allowing sugars and other low molecular weight molecules to pass through the membrane.
With a pore size range between 0.01 and 0.1 µm, the pore sizes of the ultrafiltration membrane lie between nanofiltration and microfiltration. Polymeric ultrafiltration membranes have temperature resistance and a low tendency to scale.
-
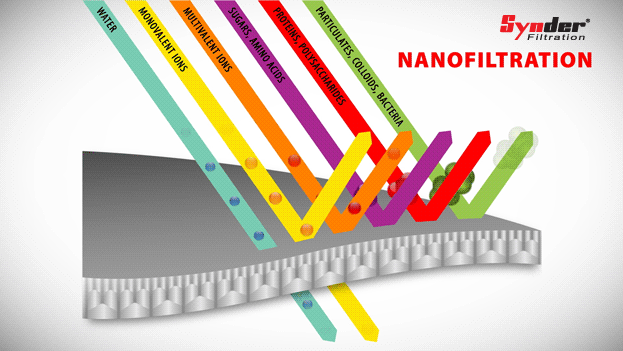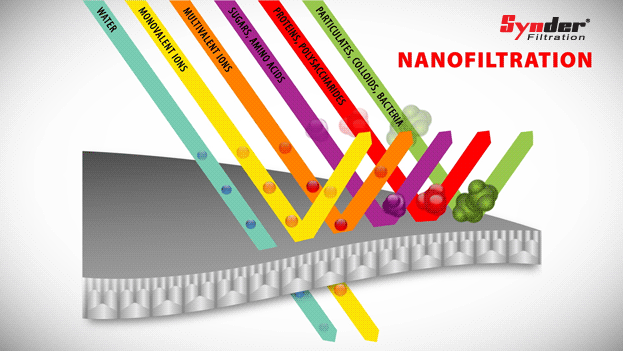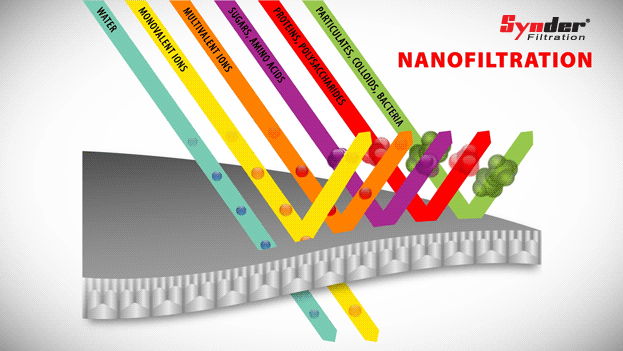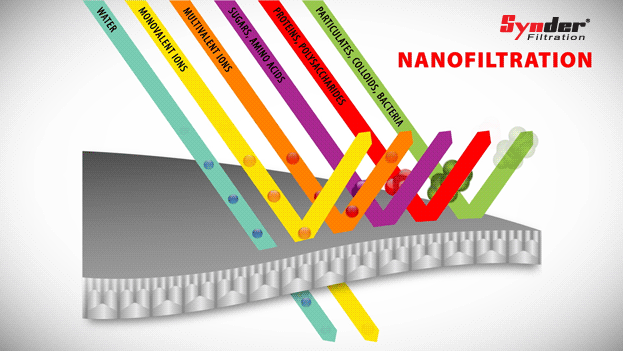
Nanofiltration
Nanofiltration is a separation process characterized by organic thin film composite membranes with a pore size range of 0.1 to 10 nm.
Unlike reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, which reject all solutes, NC membranes can operate at lower pressures and offer selective solute rejection based on size and load.
PHOTO GALLERY
DISCOVER ALL OUR PORTFOLIO








KNOW MORE!
Get in touch with our sales team.